📄 Print pdf
00971504825082
Coulomb's Law
Coulomb's Law and Electric Force
Coulomb's Law
Factors Affecting Electric Force
Factors Affecting Electric Force Between Two Charges
Coulomb's Law:
\[F=K.\frac{q_1.q_2}{r^2}\]
Main Factors:
-
Magnitude of Charges (q₁ and q₂):
Directly proportional to the product of the charges
Example: If one charge doubles
→ Force doubles
-
Distance Between Them (r):
Inversely proportional to the square of the distance
Example: If distance doubles
→ Force reduces to one-fourth
-
Medium (k):
Dielectric constant depends on the medium:
k = 1/(4πε₀εᵣ)
where εᵣ is the relative permittivity of the medium
Mathematical Relationships:
- \[F ∝ q₁q₂ \](Direct)
- \[F ∝\frac { 1}{r²} \](Inverse square)
- \[F ∝ \frac {1}{εᵣ }\](Inverse with medium permittivity)
Electric Force Between Charges
Electric Force Between Two Charges
Coulomb's Law
The electric force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of their magnitudes and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them:
\[F=K.\frac{q_1.q_2}{r^2}\]
Where:
k = Coulomb's constant ≈ 8.9875×10⁹ N·m²/C²
Types of Electric Forces
1. Attractive Force
Occurs when the charges are of opposite types (one positive and one negative)
Example: Attraction between electrons and nucleus in an atom
2. Repulsive Force
Occurs when the charges are of the same type (both positive or both negative)
Example: Repulsion between two similarly charged balloons
Important Properties
- Mutual force (equal in magnitude and opposite in direction)
- Central force (acts along the line joining the charges)
- Decreases with increasing distance between charges
- Depends on the insulating medium between charges
Practical Applications
- Design of electronic circuits
- Operation of capacitors
- Lightning phenomenon
- Laser printers
Important Notes:
1. Force is repulsive if charges are similar
2. Force is attractive if charges are different
3. Force unit: Newton (N)
4. Mutual interaction follows Newton's third law
Electric Force Between Three Charges
Electric Force Between Three Charges in a Straight Line
Coulomb's Law:
Force between two charges:
\[F=K.\frac{q_1.q_2}{r^2}\]
Resultant Force Determination:
- Determine force direction between each pair (repulsion ←← or attraction →←)
- Calculate force magnitude between each pair using the law
- Vectorially sum the forces according to their directions
Direction Determination Table (for middle charge):
Charge Arrangement
Force Direction
Example
(+ , + , +)
← if closer to left, → if closer to right
Q1=+2C, Q2=+3C, Q3=+5C
(- , - , -)
→ if closer to left, ← if closer to right
Q1=-4C, Q2=-1C, Q3=-3C
(+ , + , -)
← from left (repulsion), → from right (attraction)
Q1=+5C, Q2=+2C, Q3=-6C
(- , + , +)
→ from left (attraction), ← from right (repulsion)
Q1=-3C, Q2=+4C, Q3=+1C
Notes:
- Charge sign determines force type (repulsion/attraction)
- Distance between charges determines force strength
- Resultant direction is determined by comparing force magnitudes
Electric Force in a Right Triangle
Analysis of Electric Forces in a Right Triangle
Geometric Configuration:
Three point charges (q₁, q₂, q₃) placed at:
- q₁ and q₂ at the short sides
- q₃ at the right angle vertex (90° angle)
Basic Coulomb's Law:
\[F=K.\frac{q_1.q_2}{r^2}\]
where kₑ = 8.99×10⁹ N·m²/C²
Steps to Calculate Resultant on q₃:
- Calculate force between q₁ and q₃ \[F_{12}=K.\frac{q_1.q_2}{a^2}\]
- Calculate force between q₂ and q₃: \[F_{23}=K.\frac{q_2.q_3}{b^2}\]
- Resolve forces into components:
- F₁₃ → horizontal (F₁₃x) and vertical (F₁₃y) components
- F₂₃ → horizontal (F₂₃x) and vertical (F₂₃y) components
- Total resultant:
\[Fₜₒₜₐₗ_x = ΣFₓ\]
\[Fₜₒₜₐₗ_y = ΣFᵧ\]
Resultant Direction:
\[ θ = tan^{-1}\frac {(Fₜₒₜₐₗ_y )}{ (Fₜₒₜₐₗ_x)}\]
Important Notes:
- Consider charge signs (attraction/repulsion)
- Calculate distances using Pythagorean theorem when needed
- Direction depends on charge nature:
Charge Types
Force Direction
Same
Repulsion
Different
Attraction
Coulomb's Law Simulation
Force Between Two Charges
Three Charges in a Straight Line
Right Triangle
Resultant Electric Force
Coulomb's Law |
Coulomb's Law
Factors Affecting Electric Force Between Two Charges
Coulomb's Law:
Main Factors:
-
Magnitude of Charges (q₁ and q₂):
Directly proportional to the product of the charges
Example: If one charge doubles
→ Force doubles -
Distance Between Them (r):
Inversely proportional to the square of the distance
Example: If distance doubles
→ Force reduces to one-fourth -
Medium (k):
Dielectric constant depends on the medium:
k = 1/(4πε₀εᵣ)
where εᵣ is the relative permittivity of the medium
Mathematical Relationships:
- \[F ∝ q₁q₂ \](Direct)
- \[F ∝\frac { 1}{r²} \](Inverse square)
- \[F ∝ \frac {1}{εᵣ }\](Inverse with medium permittivity)
Electric Force Between Two Charges
Coulomb's Law
The electric force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of their magnitudes and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them:
\[F=K.\frac{q_1.q_2}{r^2}\]
Where:
k = Coulomb's constant ≈ 8.9875×10⁹ N·m²/C²
Types of Electric Forces
1. Attractive Force
Occurs when the charges are of opposite types (one positive and one negative)
Example: Attraction between electrons and nucleus in an atom
2. Repulsive Force
Occurs when the charges are of the same type (both positive or both negative)
Example: Repulsion between two similarly charged balloons
Important Properties
- Mutual force (equal in magnitude and opposite in direction)
- Central force (acts along the line joining the charges)
- Decreases with increasing distance between charges
- Depends on the insulating medium between charges
Practical Applications
- Design of electronic circuits
- Operation of capacitors
- Lightning phenomenon
- Laser printers
Important Notes:
1. Force is repulsive if charges are similar
2. Force is attractive if charges are different
3. Force unit: Newton (N)
4. Mutual interaction follows Newton's third law
Electric Force Between Three Charges in a Straight Line
Coulomb's Law:
Force between two charges: \[F=K.\frac{q_1.q_2}{r^2}\]
Resultant Force Determination:
- Determine force direction between each pair (repulsion ←← or attraction →←)
- Calculate force magnitude between each pair using the law
- Vectorially sum the forces according to their directions
Direction Determination Table (for middle charge):
| Charge Arrangement | Force Direction | Example |
|---|---|---|
| (+ , + , +) | ← if closer to left, → if closer to right | Q1=+2C, Q2=+3C, Q3=+5C |
| (- , - , -) | → if closer to left, ← if closer to right | Q1=-4C, Q2=-1C, Q3=-3C |
| (+ , + , -) | ← from left (repulsion), → from right (attraction) | Q1=+5C, Q2=+2C, Q3=-6C |
| (- , + , +) | → from left (attraction), ← from right (repulsion) | Q1=-3C, Q2=+4C, Q3=+1C |
Notes:
- Charge sign determines force type (repulsion/attraction)
- Distance between charges determines force strength
- Resultant direction is determined by comparing force magnitudes
Analysis of Electric Forces in a Right Triangle
Geometric Configuration:
Three point charges (q₁, q₂, q₃) placed at:
- q₁ and q₂ at the short sides
- q₃ at the right angle vertex (90° angle)
Basic Coulomb's Law:
\[F=K.\frac{q_1.q_2}{r^2}\]where kₑ = 8.99×10⁹ N·m²/C²
Steps to Calculate Resultant on q₃:
- Calculate force between q₁ and q₃ \[F_{12}=K.\frac{q_1.q_2}{a^2}\]
- Calculate force between q₂ and q₃: \[F_{23}=K.\frac{q_2.q_3}{b^2}\]
- Resolve forces into components:
- F₁₃ → horizontal (F₁₃x) and vertical (F₁₃y) components
- F₂₃ → horizontal (F₂₃x) and vertical (F₂₃y) components
- Total resultant:
\[Fₜₒₜₐₗ_x = ΣFₓ\]
\[Fₜₒₜₐₗ_y = ΣFᵧ\]
Resultant Direction:
\[ θ = tan^{-1}\frac {(Fₜₒₜₐₗ_y )}{ (Fₜₒₜₐₗ_x)}\]
Important Notes:
- Consider charge signs (attraction/repulsion)
- Calculate distances using Pythagorean theorem when needed
- Direction depends on charge nature:
Charge Types Force Direction Same Repulsion Different Attraction
 Physics
Physics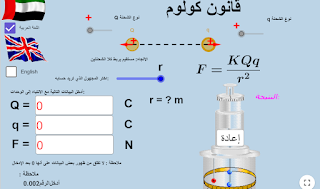
No comments:
Post a Comment