Question Bank: Electric Potential and Potential Energy |
📄 Print PDF
00971504825082
\[1 \star\]
The electric potential energy of a positive charge increases when it moves
Perpendicular to the field -C
In the direction of the field -A
In the direction of the electric force -D
Opposite to the field -B
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
\[2 \star\]
A positive charge (proton) is moved between two points
\[A\;\;\Rightarrow\;\;B\]
Coordinates of the points:
\[A=(2\;m,-3\;m)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;B=(-2\;m,2\;m)\]
In a uniform electric field of intensity:
\[E=4× 10^3\;\;N/C\]
Directed toward the negative vertical axis as shown below. The change in electric potential energy equals:
\[ q_p = 1.6 ×10^{-19}C\]

\[∆ 𝑈= - 2.56 × 10^{-15}\;\; J \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ ∆ 𝑈= 3.2 × 10^{-15}\;\; J \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[∆ 𝑈= - 3.2 × 10^{-15}\;\; J \;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ ∆ 𝑈= 2.56 × 10^{-15}\;\; J \;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
\[3\star\]
A capacitor with plates has an electric field intensity between them of:
\[E=500 \;\;N/C\] and the distance between them is
\[15\;\;Cm\] as shown below. The electric potential energy of an electron at a point 5 cm from the negative plate equals:
\[q_e=-1.6 × 10^{-19}\;\;c\]

\[u= 4 × 10^{-18}\;\;J \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[u= 1.2 × 10^{-17}\;\;J \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[u= 0.6 × 10^{-17}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[u= 8 × 10^{-18}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
\[4 \star \star\]
An electron and proton are separated by
\[2\;\;𝝁m\]
The work done to increase the distance between them to
\[4\;\;Cm\]

\[ W = -1.15 × 10^{-22}\;\;J \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[W = -4.24 × 10^{-22}\;\;J \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[W = 3.64 × 10^{-22}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ W = 2.25 × 10^{-22}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
\[5 \star \]
An electron moved between two points in an electric field. If it started with a velocity of
\[A\Rightarrow\;\;v_A=80 \frac{m}{s}\]
and its velocity at point B became
\[B\Rightarrow\;\;v_B=10^5\frac{m}{s}\]
Calculate the potential difference between the two points given that
\[q_e= - 1.6×10^{-19}C , m_e=9.1×10^{-31}kg\]

\[ ∆𝑉=- 0.03\;\; V \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[∆𝑉= 0.01\;\; V \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[ ∆𝑉= -0.04\;\; V \;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ ∆𝑉= 0.02\;\; V \;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
\[6 \star\]
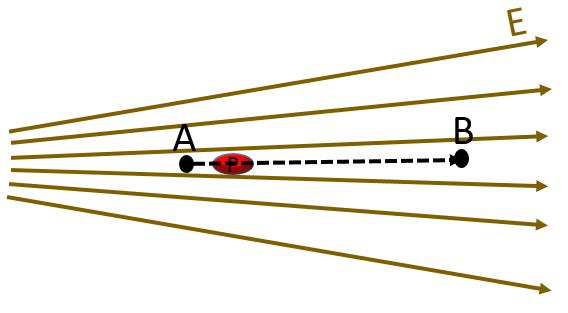
A proton was allowed to move between two points with a potential difference of
\[∆𝑉= 500\;\; V \]The final velocity of the proton equals
Given that \[q_P= 1.6×10^{-19}C , m_P=1.67×10^{-27}kg\]
\[𝑣_𝑓=1.2 × 10^5 \;\;m/s \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[𝑣_𝑓=5.2 × 10^5 \;\;m/s \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[ 𝑣_𝑓=1.8 × 10^5 \;\;m/s \;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ 𝑣_𝑓=3.1 × 10^5 \;\;m/s \;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
\[7 \star\]
\[A\;\;\;,B\]Two points
inside an electric field \[V_A= 100 V , V_B=60 V \]A proton was moved from point \[A\Rightarrow B \] Then one of the following answers correctly expresses the movement of the proton in the field

\[ ΔU = 6.4 × 10^{-18}\;\;J \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ΔK= 6.4 × 10^{-18}\;\;J \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[W = 3.64 × 10^{-22}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ ΔV_(AB)=40\;\;V\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
\[8 \star \star\]
The potential at point A was calculated
\[A\;\;\;\; V_A= -45 V \] and the field at the same point was calculated to be \[E=112.5 \;\;N/C\]
Then the magnitude and type of charge affecting that point equals

\[q= -2 × 10^{-9}\;\;C\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[q= 4 × 10^{-9}\;\;C \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[q= -4 × 10^{-9}\;\;C\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ q= 2 × 10^{-9}\;\;C\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
\[9 \star \star\]
In the figure below, an electron was transferred from point
\[A\Rightarrow B \] The work done equals
Given that \[q_e= - 1.6×10^{-19}C \]

\[q= W= 4.32 × 10^{-17}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ W= - 4.32 × 10^{-17}\;\;J \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[ W= 5.32 × 10^{-17}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ W= -5.32 × 10^{-17}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
\[10 \star \star\]
In the figure below, there are two charges:
\[q_1= -4 \;\;nC\;\;\;,\;\;\;q_2=6\;\;nC\]
The first charge is negative and placed at the origin point,
and the second charge is positive and placed at a point
\[0.4\;\;m\] away from the origin.
The point of zero potential on the line connecting
the two charges is located at position:

\[ X=0.14 \;\;m \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ X=0.12 \;\;m \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[ X=0.18\;\; m\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ X=0.16\;\; m \;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
\[11 \star \star \star\]
For a parallel plate capacitor, the potential difference between the plates is
\[ ∆𝑉= 150 \;\; V\]
and the distance between the plates is
\[6\;\;Cm\] then the potential at a point
located at a distance from the positive plate
\[X_A= 2\;\; Cm \] equals

\[VA=50\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[VA=120\;\; V \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[ VA=100\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ VA=80\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
\[12 \star \star\]
In the figure below, a uniform field with intensity
\[ E = 500 \;\;N/C \]
then the potential difference between points
\[∆𝑉_{𝐴𝐵}=?\]
and the dimensions are shown in the figure equals

\[∆𝑉(𝐴𝐵)=-200\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[∆𝑉(𝐴𝐵)=-150\;\; V \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[ ∆𝑉(𝐴𝐵)=200\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ ∆𝑉(𝐴𝐵)=150\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
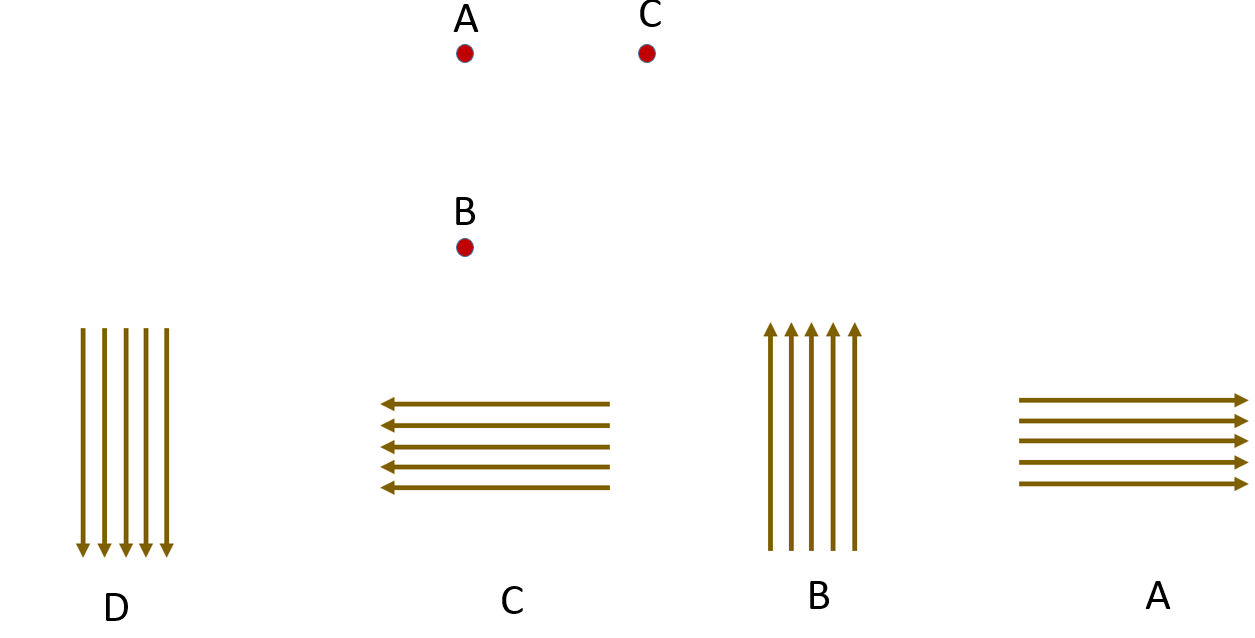
\[13 \star\]
Three points inside a uniform field as shown in the figure below, one of the lines represents the correct shape of the uniform field lines given that \[ 0 > ∆𝑉_{𝐴𝐵} , ∆𝑉_{𝐴C}= 0\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
\[14 \star \star\]
A charged particle was moved from point
\[A\Rightarrow B\]
The work done to move the charged particle is:

\[0>W\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ W>0 \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
Cannot determine work because the particle's charge is unknown -D
\[ W=0\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
\[15 \star\]
The figure below shows equipotential surface lines. The maximum electric field magnitude
at point \[K\] in the figure

 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
\[16 \star \star\]
A uniformly charged wire with linear charge density
\[ λ= 4×10^{-8}\;\;C/m\] is bent into a quarter-circle of radius R. The potential at the center of curvature is:
\[R\]

\[V=565.5 \;\;V\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ V=322.2 \;\; V \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[ V=630.4\;\;V\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ V=1131\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
\[17 \star \star \star\]
The electric potential in a region of space is given by the relation:
\[V(X,Y,Z)=5X^2+8XY+7Z\]
The value of the electric field at a point with coordinates
\[(5,-2,-3)\]
equals:
\[E =67.2\;\; N/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[E =52.9\;\; N/C \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[ E =32.8 \;\;N/C \;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ E =64.5 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
\[18 \star \star \star\]
A small charged body with charge
\[ 3 \;\;µC\]
placed at point
\[ X= 1\;\; m \]
in a region where the electric potential varies according to
the relation \[ V_{x}= 4-3X^3\] then the electric force acting on the particle equals
\[F= 6.5 × 10^{-5}\;\;N\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[F= 3.6 × 10^{-5}\;\;N \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[F= 4.5 × 10^{-5}\;\;N\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ F=2.7 × 10^{-5}\;\;N\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
\[19 \star \star \star\]
In the figure below, three equal magnitude charges are placed \[q_1=q_2=q_3=2\;\;nC\]
on the vertices of a right-angled triangle with dimensions shown in the drawing
then the work done to bring the charge at the right angle vertex
from infinity to its current position equals

\[𝑊=- 7.1 × 10^{-7}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[𝑊=+ 5.2 × 10^{-7}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[𝑊=- 2.1 × 10^{-7}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ 𝑊=+3.6 × 10^{-7}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
\[20 \star \star\]
Three charges located at the vertices
of a right-angled triangle as shown in the figure below
\[q_1=-8\;\;nc\;\;\;q_2=-6\;\;nc\;\;\;q_3=3\;\;nc\]

Then the potential energy of the system consisting of three charges
\[ U=+2.85 × 10^{-7}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ U=+5.67 × 10^{-7}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[ U=+7.44 × 10^{-7}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ U=+3.45 × 10^{-7}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
\[21 \star\]
A spherical conductor with radius
\[R=0.5\;\;m\] and the field strength on the conductor's surface equals
\[ E=5000 \;\;N/C\] then the potential at a point distant from the conductor's center
\[0.2\;\;m\]equals

\V=2500 \;\;V\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ V=0.0 \;\; V \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[ V= V=1500\;\;V\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ V=10000\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
\[22 \star \star \star\]
The following figure represents the electric potential as a function of the horizontal axis coordinates

The correct drawing of the corresponding electric field as a function of the horizontal axis

 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
\[23 \star\]
An electric charge
\[Q\]was placed at the origin. What is the ratio of the absolute potential at point
\[A\]to the absolute potential at point
\[B\]

\[ 0.33 \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ 0.5 \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[ 3\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ 2 \;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
\[24 \star\]
Two points
\[A\;\;\;,B\] are at a distance \[r\] from two unequal charges, \[-Q\;\;\;\;+3Q\]. The work required to move a charge
\[q\] from point \[A\Rightarrow B\]

\[ W>0.0 \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
Depends on the path taken-A
\[ 0.0>W\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ W=0.0\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
\[25 \star \star\]
An electric field is created by a positive charge
.The distribution of electric field lines and equipotential lines is shown in the diagram
.Which of the following statements is correct regarding the electric potential?

\[ 𝑉_𝐴>𝑉_𝐵=𝑉_𝐶>𝑉_𝐷\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ 𝑉_D>𝑉_𝐵>𝑉_𝐶>𝑉_A \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[𝑉_D>𝑉_𝐵=𝑉_𝐶>𝑉_A\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ 𝑉_𝐴>𝑉_𝐵>𝑉_𝐶>𝑉_𝐷\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
\[26 \star \star\]
Four equal negative charges
each of magnitude \[-q\]
are arranged as shown in the figure
Calculate the net electric potential at the center of the square?

\[ V_{net}=-4\sqrt 2\frac {k.q}{r} \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ V_{net}=-\sqrt 2\frac {k.q}{r} \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[ V_{net}=0\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ V_{net}=-2\sqrt 2\frac {k.q}{r}\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
\[27 \star\]
A point charge
\[q_1=+6.0\;\; µC \] is placed at point
\[-3\;\;m\] and a second charge \[q_2=?\] is placed at point \[2\;\;m\]. The net electric potential at the origin is zero.
Then the magnitude and type of charge
\[q_2\]
equals

\[q_2= 5 \times 10^{-6}\;\;C \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[q_2= -4 \times 10^{-6}\;\;C \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[q_2= 4 \times 10^{-6}\;\;C \;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[q_2= -5 \times 10^{-6}\;\;C \;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Select the correct answer
Solve the following problems
The electric potential energy of a positive charge increases when it moves
Perpendicular to the field -C |
In the direction of the field -A |
In the direction of the electric force -D |
Opposite to the field -B |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
A positive charge (proton) is moved between two points
\[A\;\;\Rightarrow\;\;B\]
Coordinates of the points:
\[A=(2\;m,-3\;m)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;B=(-2\;m,2\;m)\]
In a uniform electric field of intensity:
\[E=4× 10^3\;\;N/C\]
Directed toward the negative vertical axis as shown below. The change in electric potential energy equals:
\[ q_p = 1.6 ×10^{-19}C\]

\[∆ 𝑈= - 2.56 × 10^{-15}\;\; J \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ ∆ 𝑈= 3.2 × 10^{-15}\;\; J \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[∆ 𝑈= - 3.2 × 10^{-15}\;\; J \;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ ∆ 𝑈= 2.56 × 10^{-15}\;\; J \;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
A capacitor with plates has an electric field intensity between them of:
\[E=500 \;\;N/C\] and the distance between them is
\[15\;\;Cm\] as shown below. The electric potential energy of an electron at a point 5 cm from the negative plate equals:
\[q_e=-1.6 × 10^{-19}\;\;c\]

\[u= 4 × 10^{-18}\;\;J \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[u= 1.2 × 10^{-17}\;\;J \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[u= 0.6 × 10^{-17}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[u= 8 × 10^{-18}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
An electron and proton are separated by
\[2\;\;𝝁m\]
The work done to increase the distance between them to
\[4\;\;Cm\]

\[ W = -1.15 × 10^{-22}\;\;J \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[W = -4.24 × 10^{-22}\;\;J \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[W = 3.64 × 10^{-22}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ W = 2.25 × 10^{-22}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
An electron moved between two points in an electric field. If it started with a velocity of \[A\Rightarrow\;\;v_A=80 \frac{m}{s}\] and its velocity at point B became \[B\Rightarrow\;\;v_B=10^5\frac{m}{s}\] Calculate the potential difference between the two points given that \[q_e= - 1.6×10^{-19}C , m_e=9.1×10^{-31}kg\]

\[ ∆𝑉=- 0.03\;\; V \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[∆𝑉= 0.01\;\; V \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[ ∆𝑉= -0.04\;\; V \;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ ∆𝑉= 0.02\;\; V \;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
A proton was allowed to move between two points with a potential difference of \[∆𝑉= 500\;\; V \]The final velocity of the proton equals Given that \[q_P= 1.6×10^{-19}C , m_P=1.67×10^{-27}kg\]

\[𝑣_𝑓=1.2 × 10^5 \;\;m/s \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[𝑣_𝑓=5.2 × 10^5 \;\;m/s \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[ 𝑣_𝑓=1.8 × 10^5 \;\;m/s \;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ 𝑣_𝑓=3.1 × 10^5 \;\;m/s \;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer

\[ ΔU = 6.4 × 10^{-18}\;\;J \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ΔK= 6.4 × 10^{-18}\;\;J \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[W = 3.64 × 10^{-22}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ ΔV_(AB)=40\;\;V\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
The potential at point A was calculated
\[A\;\;\;\; V_A= -45 V \] and the field at the same point was calculated to be \[E=112.5 \;\;N/C\]
Then the magnitude and type of charge affecting that point equals

\[q= -2 × 10^{-9}\;\;C\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[q= 4 × 10^{-9}\;\;C \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[q= -4 × 10^{-9}\;\;C\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ q= 2 × 10^{-9}\;\;C\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
In the figure below, an electron was transferred from point
\[A\Rightarrow B \] The work done equals
Given that \[q_e= - 1.6×10^{-19}C \]

\[q= W= 4.32 × 10^{-17}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ W= - 4.32 × 10^{-17}\;\;J \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[ W= 5.32 × 10^{-17}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ W= -5.32 × 10^{-17}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
In the figure below, there are two charges:
\[q_1= -4 \;\;nC\;\;\;,\;\;\;q_2=6\;\;nC\]
The first charge is negative and placed at the origin point,
and the second charge is positive and placed at a point
\[0.4\;\;m\] away from the origin.
The point of zero potential on the line connecting
the two charges is located at position:

\[ X=0.14 \;\;m \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ X=0.12 \;\;m \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[ X=0.18\;\; m\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ X=0.16\;\; m \;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
For a parallel plate capacitor, the potential difference between the plates is
\[ ∆𝑉= 150 \;\; V\]
and the distance between the plates is
\[6\;\;Cm\] then the potential at a point
located at a distance from the positive plate
\[X_A= 2\;\; Cm \] equals

\[VA=50\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[VA=120\;\; V \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[ VA=100\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ VA=80\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
In the figure below, a uniform field with intensity
\[ E = 500 \;\;N/C \]
then the potential difference between points
\[∆𝑉_{𝐴𝐵}=?\]
and the dimensions are shown in the figure equals

\[∆𝑉(𝐴𝐵)=-200\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[∆𝑉(𝐴𝐵)=-150\;\; V \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[ ∆𝑉(𝐴𝐵)=200\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ ∆𝑉(𝐴𝐵)=150\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
Three points inside a uniform field as shown in the figure below, one of the lines represents the correct shape of the uniform field lines given that \[ 0 > ∆𝑉_{𝐴𝐵} , ∆𝑉_{𝐴C}= 0\]

 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
A charged particle was moved from point
\[A\Rightarrow B\]
The work done to move the charged particle is:

\[0>W\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ W>0 \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
Cannot determine work because the particle's charge is unknown -D |
\[ W=0\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
The figure below shows equipotential surface lines. The maximum electric field magnitude
at point \[K\] in the figure

 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
A uniformly charged wire with linear charge density \[ λ= 4×10^{-8}\;\;C/m\] is bent into a quarter-circle of radius R. The potential at the center of curvature is: \[R\]

\[V=565.5 \;\;V\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ V=322.2 \;\; V \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[ V=630.4\;\;V\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ V=1131\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
The electric potential in a region of space is given by the relation: \[V(X,Y,Z)=5X^2+8XY+7Z\] The value of the electric field at a point with coordinates \[(5,-2,-3)\] equals:
\[E =67.2\;\; N/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[E =52.9\;\; N/C \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[ E =32.8 \;\;N/C \;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ E =64.5 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
A small charged body with charge \[ 3 \;\;µC\] placed at point \[ X= 1\;\; m \] in a region where the electric potential varies according to the relation \[ V_{x}= 4-3X^3\] then the electric force acting on the particle equals
\[F= 6.5 × 10^{-5}\;\;N\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[F= 3.6 × 10^{-5}\;\;N \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[F= 4.5 × 10^{-5}\;\;N\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ F=2.7 × 10^{-5}\;\;N\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
In the figure below, three equal magnitude charges are placed \[q_1=q_2=q_3=2\;\;nC\]
on the vertices of a right-angled triangle with dimensions shown in the drawing
then the work done to bring the charge at the right angle vertex
from infinity to its current position equals

\[𝑊=- 7.1 × 10^{-7}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[𝑊=+ 5.2 × 10^{-7}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[𝑊=- 2.1 × 10^{-7}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ 𝑊=+3.6 × 10^{-7}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
Three charges located at the vertices of a right-angled triangle as shown in the figure below \[q_1=-8\;\;nc\;\;\;q_2=-6\;\;nc\;\;\;q_3=3\;\;nc\]

Then the potential energy of the system consisting of three charges
\[ U=+2.85 × 10^{-7}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ U=+5.67 × 10^{-7}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[ U=+7.44 × 10^{-7}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ U=+3.45 × 10^{-7}\;\;J\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
A spherical conductor with radius \[R=0.5\;\;m\] and the field strength on the conductor's surface equals \[ E=5000 \;\;N/C\] then the potential at a point distant from the conductor's center \[0.2\;\;m\]equals

\V=2500 \;\;V\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ V=0.0 \;\; V \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[ V= V=1500\;\;V\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ V=10000\;\; V\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
The following figure represents the electric potential as a function of the horizontal axis coordinates


 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
An electric charge
\[Q\]was placed at the origin. What is the ratio of the absolute potential at point
\[A\]to the absolute potential at point
\[B\]

\[ 0.33 \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ 0.5 \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[ 3\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ 2 \;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
Two points
\[A\;\;\;,B\] are at a distance \[r\] from two unequal charges, \[-Q\;\;\;\;+3Q\]. The work required to move a charge
\[q\] from point \[A\Rightarrow B\]

\[ W>0.0 \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
Depends on the path taken-A |
\[ 0.0>W\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ W=0.0\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
An electric field is created by a positive charge
.The distribution of electric field lines and equipotential lines is shown in the diagram
.Which of the following statements is correct regarding the electric potential?

\[ 𝑉_𝐴>𝑉_𝐵=𝑉_𝐶>𝑉_𝐷\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ 𝑉_D>𝑉_𝐵>𝑉_𝐶>𝑉_A \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[𝑉_D>𝑉_𝐵=𝑉_𝐶>𝑉_A\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ 𝑉_𝐴>𝑉_𝐵>𝑉_𝐶>𝑉_𝐷\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
Four equal negative charges
each of magnitude \[-q\]
are arranged as shown in the figure
Calculate the net electric potential at the center of the square?

\[ V_{net}=-4\sqrt 2\frac {k.q}{r} \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ V_{net}=-\sqrt 2\frac {k.q}{r} \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[ V_{net}=0\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ V_{net}=-2\sqrt 2\frac {k.q}{r}\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
A point charge
\[q_1=+6.0\;\; µC \] is placed at point
\[-3\;\;m\] and a second charge \[q_2=?\] is placed at point \[2\;\;m\]. The net electric potential at the origin is zero.
Then the magnitude and type of charge
\[q_2\]
equals

\[q_2= 5 \times 10^{-6}\;\;C \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[q_2= -4 \times 10^{-6}\;\;C \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[q_2= 4 \times 10^{-6}\;\;C \;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[q_2= -5 \times 10^{-6}\;\;C \;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Select the correct answer
 Physics
Physics