Electric Field and Gauss's Law Question Bank |

📄 Print pdf
00971504825082
1

One of the following measurement units is equivalent to the electric field measurement unit
\[Kg.m.A^{-1}.s^{-2}\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[Kg.m.A^{-1}.s^{-3}\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[Kg.m.A^{-1}.s^{-1}\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[Kg.m.A^{-2}.s^{-2}\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
2

An electric field with intensity \[E=500\frac{N}{C}\] has an electron placed inside it. The electric force acting on the electron equals:
\[q_e=1.6×10^{-19}C\]

\[Fe=4×10^{-17} \;\;N\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
Opposite to the field direction
\[Fe=4×10^{-17} \;\;N\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
In the field direction
\[Fe=8×10^{-17} \;\;N\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
Opposite to the field direction
\[Fe=8×10^{-17} \;\;N\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
In the field direction
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
3

In the figure below, two charges are on the same line \[q_1=+9\;\;nc\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;q_2=?\] At point \[A\]
the electric field is canceled. The magnitude and type of charge
\[q_2\] equals

\[q_2= - 3.2 ×10^{-7}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[q_2= + 1.44 ×10^{-7}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[q_2= -4.5 ×10^{-7}\;\;c;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[q_2= + 2.25 ×10^{-7}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
4

In the figure below, the field at point \[A\] was calculated
\[E_{net}=500\frac{N}{C}\]
and its direction is shown in the drawing. If the magnitude of the electric field
produced by the first charge equals
\[E_{1}=300\frac{N}{C}\]then the type
and magnitude of the second charge equals

\[q_2= - 3.24 ×10^{-9}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[q_2= - 2.43 ×10^{-9}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[q_2= + 1.78 ×10^{-9}\;\;c;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[q_2= + 5.67 ×10^{-9}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
5

In the figure below, the field lines for three charges are drawn.
One of the following answers is correct

\[q_1(-)\;\;\;\;q_2(+)\;\;\;\;q_3(+) \;\;\;\;\;q_3>q_1>q_2\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[q_1(+)\;\;\;\;q_2(-)\;\;\;\;q_3(-)\;\;\;\;\;q_1=q_2=q_3\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[q_1(+)\;\;\;\;q_2(-)\;\;\;\;q_3(-) \;\;\;\;\;q_1>q_2=q_3\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[q_1(+)\;\;\;\;q_2(-)\;\;\;\;q_3(-)\;\;\;\;\;q_2>q_1>q_3\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
6

(1 ×10-10m ) A dipole with distance between its poles
( 0.4 m ) The field produced by the dipole was calculated at a point distant from the center of the dipole and along the dipole axis
The field intensity was \[E= 9×10^{-18}\frac{N}{C}\]then the dipole charge equals

\[q= 3.2 ×10^{-19}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[q= 2.6 ×10^{-19}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[q= 1.3 ×10^{-19}\;\;c;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[q= 6.4 ×10^{-19}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
Choose the correct answer
7

A positively charged particle is placed inside the field shown in the figure below. One of the following answers represents the motion of the particle:

The particle moves with - C
increasing acceleration
The particle moves with - A
constant velocity
The particle moves with - D
decreasing acceleration
The particle moves with - B
constant acceleration
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
8


A ball with mass (5g) is dropped to the ground while charged with a charge of (5 µc). The uniform electric field vector that makes it balanced is:

\[E= 1×10^3 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\downarrow\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
Downward
\[E= 9.8×10^3 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\downarrow\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
Downward
\[E= 1×10^3 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\uparrow\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
Upward
\[E= 9.8×10^3 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\uparrow\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
Upward
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
9


An electron is projected into a uniform electric field with intensity (E= 1 × 103N/C)
directed towards the positive vertical axis as shown in the figure below
with a speed of (𝜗=5 × 106m/s) horizontally
and travels a horizontal distance of (8 cm).
In the same time period, it will have a vertical displacement of:

\[ ∆𝑌= 0.011 \;\;m\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ ∆𝑌= 0.033 \;\;m\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[ ∆𝑌= 0.044 \;\;m\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ ∆𝑌= 0.022\;\;m\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
10

One of the following shapes has zero torque for an electric dipole in a uniform electric field

 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
11

( τ= 1.5 × 10-9N.m ) An electric dipole has maximum torque when
(positive z-axis) and is directed along the
(positive y-axis) in a uniform electric field directed along the
( E = 1 × 10-3N/C ) with magnitude

\[P=1.5×10^{-6} \;\;c.m\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
along the positive horizontal axis
\[ P=1.5×10^{-8} \;\;c.m\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
along the positive horizontal axis
\[P=1.5×10^{-8} \;\;c.m\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
along the negative horizontal axis
\[P=1.5×10^{-6} \;\;c.m\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
along the negative horizontal axis
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
12


(0.3 m) An infinite wire has an electric field calculated at a point
( 2.5 × 103N/C ) The electric field magnitude was
and direction is shown in the figure. The number of electrons gained or lost per unit length equals

\[n=2.6×10^{11}\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
Gained electrons
\[ n=2.6×10^{11} \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
Lost electrons
\[n=3.4×10^{11}\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
Gained electrons
\[n=3.4×10^{11}\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
Lost electrons
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
13


One of the following units is a unit of electric flux
\[Kg.m .A^{-1}.S^{-3}\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[Kg.m^2 .A^{-1}.S^{-3}\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[Kg.m^3 .A^{-1}.S^{-3}\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[Kg.m^2 .A^{-1}.S^{-2}\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
14

A spherical shell is charged with a charge of
\[-4\;\;µc\] and a charge is placed inside it
\[+4\;\;µc\]>then the internal charge
\[q_1=?\]
and external charge of the spherical shell \[q_2=?\]
respectively

\[q_1=+4\;µc \;\;\;\;\;q_2=+4\;µc\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[q_1=0.0 \;\;\;\;\;q_2=0.0\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[q_1=-4\;µc \;\;\;\;\;q_2=0.0\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[q_1=-4\;µc \;\;\;\;\;q_2=+4\;µc\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
15


( A ) Two infinite wires in length with charge densities and dimensions shown in the figure below. The point has a field intensity equal to

\[ E= 4200 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\longrightarrow\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
To the right
\[ E= 2800 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\longleftarrow \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
To the left
\[E= 4800 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\longrightarrow\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
To the right
\[E= 3500 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\longleftarrow\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
To the left
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solutionChoose the correct answer
16

Two infinite parallel conducting plates charged with equal charge density.
One of the following answers is correct:

\[ EA=EB=EC=ED \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[EA=EC=0 \;\;\;\;\;, \;\;\;\;\;EB=ED≠0\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[ EA=EB \;\;\;\;\;, \;\;\;\;\;ED=EC\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[EA>EC \;\;\;\;\;, \;\;\;\;\;EB=ED \;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution Choose the correct answer
17


Two infinite unconnected plates with the same charge.
The electric field at point A was calculated to be \[E= 1×10^3\frac{N}{C}\]. The charge density on each plate is:

\[𝛿= 3.6 ×10^{-9} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[𝛿= 3.9×10^{-8} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[𝛿= 4.8×10^{-9} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[𝛿= 8.85×10^{-9} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solutionChoose the correct answer
17


Two infinite unconnected plates with the same charge.
The electric field at point A was calculated to be \[E= 1×10^3\frac{N}{C}\]. The charge density on each plate is:

\[𝛿= 3.6 ×10^{-9} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[𝛿= 3.9×10^{-8} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[𝛿= 4.8×10^{-9} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[𝛿= 8.85×10^{-9} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solutionChoose the correct answer
18


An infinite conducting plate with a charge density of
\[6 × 10^{-6} \;\;C/m^2\] was left.
A positively charged sphere with a charge of
\[+4\;\;nc\] and a mass of
\[9 \;\;g\] falls towards the plate.
The sphere moves with an acceleration of

\[ a=6.37 \;\;m/s^2\;\;\;\;\;\uparrow \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
Upwards
\[ a=3.92 \;\;m/s^2\;\;\;\;\;\uparrow \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
Upwards
\[a=4.52 \;\;m/s^2\;\;\;\;\;\downarrow \;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
Downwards
\[a=9.48 \;\;m/s^2\;\;\;\;\;\downarrow \;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
Downwards
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
19



An uncharged spherical shell with an inner radius
\[0.5\;] and an outer radius
\[0.7\; m\] A point charge was placed inside it as shown in the figure below with a magnitude of
\[-6\;µc \] at its center. The electric field intensity at a point located at a distance of
\[0.6\; m \]

\[ E=0.0\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ E = 2.3 ×10^5 \;\;N/C \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[ E = 1.5 ×10^5 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[ E = 4.6 ×10^5 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
20


The relationship between the electric field and the distance from the surface of a hollow conducting sphere was plotted, resulting in the following graph. The conductor is charged with a charge of

\[q= 1.34×10^{-19} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ q= 2.56×10^{-19} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[q= 2.14×10^{-19} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[q= 1.78×10^{-19} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
21



The relationship between the electric field and the distance from the center of a charged sphere
with a non-conducting solid was plotted, resulting in the following graph. The magnitude of the electric field at
a point located at a distance
\[0.15\;m\] from the center of the sphere is equivalent to

\[E=2800 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[E=3000 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[E=2700 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[E=2900 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
22



The relationship between the electric field and distance from the center
of a uniformly charged solid non-conducting sphere was plotted,
resulting in the following graph.
The amount of charge contained within a radius of
\[0.1\;m\]
of the sphere is equivalent to:

\[q= 2.2×10^{-9} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ q= 2.45×10^{-9} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[q= 7.45×10^{-9} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[q= 1.78×10^{-9} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
23



A solid non-conducting sphere is uniformly charged with radius
\[R=0.5\;\; m\]. The field at a point \[r=0.3\;\; m\] from the center of the sphere was calculated to be \[E=4×10^3\frac{N}{C}\]. The charge of the sphere is equivalent to:

\[q= 3.54×10^{-6} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ q= 5.71×10^{-6} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[q= 1.85×10^{-6} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[q= 6.28×10^{-6} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
24



A spherical shell has a charge of
\[-7 \;\;µc \], inner radius
\[2 \;\;m\] and outer radius
\[4\;\;M\]. The electric field at a point was calculated to be
\[E= 3 ×10^3\;\;N/C\] and directed towards the shell. The charge inside the spherical shell is equivalent to:

\[q= +1.67 ×10^{-6} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ q= +5.33 ×10^{-6} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[q= -1.67×10^{-6} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[q= -5.33×10^{-6} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
25


An electric charge
generates an electric field around it. The electric field at point
\[A\] was calculated to be \[ E= 6×10^4\;\;N/C \]. The electric field at point
\[B\] was calculated to be
\[ E= 3×10^4\;\;N/C \]. The ratio between the distances
\[\frac{r_A}{r_B}\] is equal to:

\[\frac{r_A}{r_B}=0.5\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[\frac{r_A}{r_B}=0.4\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[\frac{r_A}{r_B}=0.25\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[\frac{r_A}{r_B}=0.7\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
26

In the figure below, a point charge generates an electric field around it. The ratio between the field at point
\[A\] to the field at point
\[B\]
is equal to:
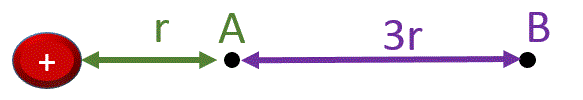
\[\frac{E_A}{E_B}=9\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[\frac{E_A}{E_B}=4\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[\frac{E_A}{E_B}=16\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[\frac{E_A}{E_B}=3\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
27

The figure shows four Gaussian surfaces surrounding charge distributions. Which Gaussian surface has no electric flux through it?

 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
28

A Gaussian surface shaped like a bean is placed in four different regions of an electric field. This is illustrated by the field lines below.

In which case is the total electric flux through the closed surface the highest?
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
29

A positive point charge (+4q)
and a negative point charge (-3q) are placed inside a conducting sphere
and a negative point charge is placed outside the sphere
with magnitude
One of the following answers
correctly represents the results of Gauss's law

Both charges affect with the same -C
force but in opposite directions
The charge inside the conductor -A
affects with a greater force on
the charge outside the conductor
The charge inside the conductor will -D
not be affected by a force and the charge
outside the conductor is affected by a force
The charge outside the conductor -B
affects with a greater force on
the charge inside the conductor
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
30

(∅=3 ×102N.m2/c ) A charge was placed inside a spherical surface and the flux
on the surface was calculated to be
If the radius of the spherical surface is doubled, the flux on the new surface
becomes

\[∅= 6 ×10^2 \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ ∅= 12 ×10^2 \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[∅= 3 ×10^2 \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[∅= 1.5×10^2 \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
31


An electric field with intensity given by the relation \[E=8\hat{X}+3\hat{Y}+4\hat{Z}(\frac{N.m^2}{c})\]
(10 cm) The flux through the right side surface of a cube with edge length
equals

\[∅= 6 ×10^{-2} \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ ∅= 8 ×10^{-2 }\;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[∅= 2 ×10^{-2} \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[∅= 4×10^{-2} \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution Choose the correct answer
32

A hollow conducting sphere with radius \[0.2\;\;m\] was uniformly charged, losing a number of electrons equal to \[n= 5×10^{12}\] electrons. The charge density on the conductor's surface equals:
Given that \[q_e=1.6×10^{-19} c\]

\[𝛿= 1.6 ×10^{-6} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[𝛿= 4.8 ×10^{-6} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[𝛿= 3.6 ×10^{-6} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[𝛿= 6 ×10^{-6} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution Choose the correct answer
33

A semi-cylinder made of insulating material with small base radius (0.1 m) and large base radius (0.2 m) was placed in a uniform electric field as shown in the figure below with intensity \[500\;\;N/C\]. The flux passing through the lateral surface of the semi-cylinder equals:

\[∅=47.1 \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ ∅=0.0 \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[∅= 25.3\;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[∅= - 35.2 \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution Choose the correct answer
34

A cube has a point charge at its center with a magnitude of
\[8 ×10^{-9}c\]. The flux through the top and bottom surfaces is equal to
\[ 𝓔_0=8.85 ×10^{-12}C.m/v\]

\[∅= 432 \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\]
\[ ∅=151 \;\;N.m^2 \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\]
\[∅= 512\;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\]
\[∅= - 301 \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\]
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
Solve the following problems
1

Two point charges on a straight line
each with magnitude \[q_1=8\;\;nc\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; q_2=?\]The electric field was calculated at point
\[A\] and its magnitude was
\[E_{net}=500 \;\;N/C\]From the figure information and previous data
What is the type of \[q_2\]
 \[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
Calculate the magnitude of charge \[q_2\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
Calculate the magnitude of charge \[q_2\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]

One of the following measurement units is equivalent to the electric field measurement unit
\[Kg.m.A^{-1}.s^{-2}\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[Kg.m.A^{-1}.s^{-3}\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[Kg.m.A^{-1}.s^{-1}\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[Kg.m.A^{-2}.s^{-2}\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer

An electric field with intensity \[E=500\frac{N}{C}\] has an electron placed inside it. The electric force acting on the electron equals: \[q_e=1.6×10^{-19}C\]

\[Fe=4×10^{-17} \;\;N\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] Opposite to the field direction |
\[Fe=4×10^{-17} \;\;N\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] In the field direction |
\[Fe=8×10^{-17} \;\;N\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] Opposite to the field direction |
\[Fe=8×10^{-17} \;\;N\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] In the field direction |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer

In the figure below, two charges are on the same line \[q_1=+9\;\;nc\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;q_2=?\] At point \[A\]
the electric field is canceled. The magnitude and type of charge
\[q_2\] equals

\[q_2= - 3.2 ×10^{-7}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[q_2= + 1.44 ×10^{-7}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[q_2= -4.5 ×10^{-7}\;\;c;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[q_2= + 2.25 ×10^{-7}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer

In the figure below, the field at point \[A\] was calculated
\[E_{net}=500\frac{N}{C}\]
and its direction is shown in the drawing. If the magnitude of the electric field
produced by the first charge equals
\[E_{1}=300\frac{N}{C}\]then the type
and magnitude of the second charge equals

\[q_2= - 3.24 ×10^{-9}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[q_2= - 2.43 ×10^{-9}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[q_2= + 1.78 ×10^{-9}\;\;c;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[q_2= + 5.67 ×10^{-9}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer

In the figure below, the field lines for three charges are drawn.
One of the following answers is correct

\[q_1(-)\;\;\;\;q_2(+)\;\;\;\;q_3(+) \;\;\;\;\;q_3>q_1>q_2\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[q_1(+)\;\;\;\;q_2(-)\;\;\;\;q_3(-)\;\;\;\;\;q_1=q_2=q_3\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[q_1(+)\;\;\;\;q_2(-)\;\;\;\;q_3(-) \;\;\;\;\;q_1>q_2=q_3\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[q_1(+)\;\;\;\;q_2(-)\;\;\;\;q_3(-)\;\;\;\;\;q_2>q_1>q_3\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer

(1 ×10-10m ) A dipole with distance between its poles
( 0.4 m ) The field produced by the dipole was calculated at a point distant from the center of the dipole and along the dipole axis
The field intensity was \[E= 9×10^{-18}\frac{N}{C}\]then the dipole charge equals

\[q= 3.2 ×10^{-19}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[q= 2.6 ×10^{-19}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[q= 1.3 ×10^{-19}\;\;c;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[q= 6.4 ×10^{-19}\;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer
Choose the correct answer

A positively charged particle is placed inside the field shown in the figure below. One of the following answers represents the motion of the particle:

The particle moves with - C
|
The particle moves with - A
|
The particle moves with - D
|
The particle moves with - B
|
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer


A ball with mass (5g) is dropped to the ground while charged with a charge of (5 µc). The uniform electric field vector that makes it balanced is:

\[E= 1×10^3 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\downarrow\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] Downward |
\[E= 9.8×10^3 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\downarrow\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] Downward |
\[E= 1×10^3 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\uparrow\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] Upward |
\[E= 9.8×10^3 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\uparrow\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] Upward |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer


An electron is projected into a uniform electric field with intensity (E= 1 × 103N/C)
directed towards the positive vertical axis as shown in the figure below
with a speed of (𝜗=5 × 106m/s) horizontally
and travels a horizontal distance of (8 cm).
In the same time period, it will have a vertical displacement of:

\[ ∆𝑌= 0.011 \;\;m\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ ∆𝑌= 0.033 \;\;m\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[ ∆𝑌= 0.044 \;\;m\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ ∆𝑌= 0.022\;\;m\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer

One of the following shapes has zero torque for an electric dipole in a uniform electric field

 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer

( τ= 1.5 × 10-9N.m ) An electric dipole has maximum torque when
(positive z-axis) and is directed along the
(positive y-axis) in a uniform electric field directed along the
( E = 1 × 10-3N/C ) with magnitude

\[P=1.5×10^{-6} \;\;c.m\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] along the positive horizontal axis |
\[ P=1.5×10^{-8} \;\;c.m\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] along the positive horizontal axis |
\[P=1.5×10^{-8} \;\;c.m\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] along the negative horizontal axis |
\[P=1.5×10^{-6} \;\;c.m\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] along the negative horizontal axis |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer


(0.3 m) An infinite wire has an electric field calculated at a point
( 2.5 × 103N/C ) The electric field magnitude was
and direction is shown in the figure. The number of electrons gained or lost per unit length equals

\[n=2.6×10^{11}\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] Gained electrons |
\[ n=2.6×10^{11} \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] Lost electrons |
\[n=3.4×10^{11}\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] Gained electrons |
\[n=3.4×10^{11}\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] Lost electrons |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer


One of the following units is a unit of electric flux
\[Kg.m .A^{-1}.S^{-3}\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[Kg.m^2 .A^{-1}.S^{-3}\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[Kg.m^3 .A^{-1}.S^{-3}\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[Kg.m^2 .A^{-1}.S^{-2}\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer

A spherical shell is charged with a charge of \[-4\;\;µc\] and a charge is placed inside it \[+4\;\;µc\]>then the internal charge \[q_1=?\] and external charge of the spherical shell \[q_2=?\] respectively

\[q_1=+4\;µc \;\;\;\;\;q_2=+4\;µc\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[q_1=0.0 \;\;\;\;\;q_2=0.0\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[q_1=-4\;µc \;\;\;\;\;q_2=0.0\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[q_1=-4\;µc \;\;\;\;\;q_2=+4\;µc\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer


( A ) Two infinite wires in length with charge densities and dimensions shown in the figure below. The point has a field intensity equal to

\[ E= 4200 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\longrightarrow\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] To the right |
\[ E= 2800 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\longleftarrow \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] To the left |
\[E= 4800 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\longrightarrow\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] To the right |
\[E= 3500 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\longleftarrow\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] To the left |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solutionChoose the correct answer

Two infinite parallel conducting plates charged with equal charge density.
One of the following answers is correct:

\[ EA=EB=EC=ED \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[EA=EC=0 \;\;\;\;\;, \;\;\;\;\;EB=ED≠0\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[ EA=EB \;\;\;\;\;, \;\;\;\;\;ED=EC\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[EA>EC \;\;\;\;\;, \;\;\;\;\;EB=ED \;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution Choose the correct answer


Two infinite unconnected plates with the same charge. The electric field at point A was calculated to be \[E= 1×10^3\frac{N}{C}\]. The charge density on each plate is:

\[𝛿= 3.6 ×10^{-9} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[𝛿= 3.9×10^{-8} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[𝛿= 4.8×10^{-9} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[𝛿= 8.85×10^{-9} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solutionChoose the correct answer


Two infinite unconnected plates with the same charge. The electric field at point A was calculated to be \[E= 1×10^3\frac{N}{C}\]. The charge density on each plate is:

\[𝛿= 3.6 ×10^{-9} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[𝛿= 3.9×10^{-8} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[𝛿= 4.8×10^{-9} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[𝛿= 8.85×10^{-9} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solutionChoose the correct answer


An infinite conducting plate with a charge density of
\[6 × 10^{-6} \;\;C/m^2\] was left.
A positively charged sphere with a charge of
\[+4\;\;nc\] and a mass of
\[9 \;\;g\] falls towards the plate.
The sphere moves with an acceleration of

\[ a=6.37 \;\;m/s^2\;\;\;\;\;\uparrow \;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] Upwards |
\[ a=3.92 \;\;m/s^2\;\;\;\;\;\uparrow \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] Upwards |
\[a=4.52 \;\;m/s^2\;\;\;\;\;\downarrow \;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] Downwards |
\[a=9.48 \;\;m/s^2\;\;\;\;\;\downarrow \;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] Downwards |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer



An uncharged spherical shell with an inner radius
\[0.5\;] and an outer radius
\[0.7\; m\] A point charge was placed inside it as shown in the figure below with a magnitude of
\[-6\;µc \] at its center. The electric field intensity at a point located at a distance of
\[0.6\; m \]

\[ E=0.0\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ E = 2.3 ×10^5 \;\;N/C \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[ E = 1.5 ×10^5 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[ E = 4.6 ×10^5 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer


The relationship between the electric field and the distance from the surface of a hollow conducting sphere was plotted, resulting in the following graph. The conductor is charged with a charge of

\[q= 1.34×10^{-19} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ q= 2.56×10^{-19} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[q= 2.14×10^{-19} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[q= 1.78×10^{-19} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer



The relationship between the electric field and the distance from the center of a charged sphere
with a non-conducting solid was plotted, resulting in the following graph. The magnitude of the electric field at
a point located at a distance
\[0.15\;m\] from the center of the sphere is equivalent to

\[E=2800 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[E=3000 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[E=2700 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[E=2900 \;\;N/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer



The relationship between the electric field and distance from the center
of a uniformly charged solid non-conducting sphere was plotted,
resulting in the following graph.
The amount of charge contained within a radius of
\[0.1\;m\]
of the sphere is equivalent to:

\[q= 2.2×10^{-9} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ q= 2.45×10^{-9} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[q= 7.45×10^{-9} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[q= 1.78×10^{-9} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer



A solid non-conducting sphere is uniformly charged with radius
\[R=0.5\;\; m\]. The field at a point \[r=0.3\;\; m\] from the center of the sphere was calculated to be \[E=4×10^3\frac{N}{C}\]. The charge of the sphere is equivalent to:

\[q= 3.54×10^{-6} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ q= 5.71×10^{-6} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[q= 1.85×10^{-6} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[q= 6.28×10^{-6} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer



A spherical shell has a charge of \[-7 \;\;µc \], inner radius \[2 \;\;m\] and outer radius \[4\;\;M\]. The electric field at a point was calculated to be \[E= 3 ×10^3\;\;N/C\] and directed towards the shell. The charge inside the spherical shell is equivalent to:

\[q= +1.67 ×10^{-6} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ q= +5.33 ×10^{-6} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[q= -1.67×10^{-6} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[q= -5.33×10^{-6} \;\;c\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer


An electric charge
generates an electric field around it. The electric field at point
\[A\] was calculated to be \[ E= 6×10^4\;\;N/C \]. The electric field at point
\[B\] was calculated to be
\[ E= 3×10^4\;\;N/C \]. The ratio between the distances
\[\frac{r_A}{r_B}\] is equal to:

\[\frac{r_A}{r_B}=0.5\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[\frac{r_A}{r_B}=0.4\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[\frac{r_A}{r_B}=0.25\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[\frac{r_A}{r_B}=0.7\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer

In the figure below, a point charge generates an electric field around it. The ratio between the field at point
\[A\] to the field at point
\[B\]
is equal to:

\[\frac{E_A}{E_B}=9\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[\frac{E_A}{E_B}=4\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[\frac{E_A}{E_B}=16\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[\frac{E_A}{E_B}=3\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer

The figure shows four Gaussian surfaces surrounding charge distributions. Which Gaussian surface has no electric flux through it?
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution
Choose the correct answer

A Gaussian surface shaped like a bean is placed in four different regions of an electric field. This is illustrated by the field lines below.

In which case is the total electric flux through the closed surface the highest?
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer

A positive point charge (+4q)
and a negative point charge (-3q) are placed inside a conducting sphere
and a negative point charge is placed outside the sphere
with magnitude
One of the following answers
correctly represents the results of Gauss's law

Both charges affect with the same -C
|
The charge inside the conductor -A
|
The charge inside the conductor will -D
|
The charge outside the conductor -B
|
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer

(∅=3 ×102N.m2/c ) A charge was placed inside a spherical surface and the flux
on the surface was calculated to be
If the radius of the spherical surface is doubled, the flux on the new surface
becomes

\[∅= 6 ×10^2 \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ ∅= 12 ×10^2 \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[∅= 3 ×10^2 \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[∅= 1.5×10^2 \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer


An electric field with intensity given by the relation \[E=8\hat{X}+3\hat{Y}+4\hat{Z}(\frac{N.m^2}{c})\]
(10 cm) The flux through the right side surface of a cube with edge length
equals

\[∅= 6 ×10^{-2} \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ ∅= 8 ×10^{-2 }\;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[∅= 2 ×10^{-2} \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[∅= 4×10^{-2} \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution Choose the correct answer

A hollow conducting sphere with radius \[0.2\;\;m\] was uniformly charged, losing a number of electrons equal to \[n= 5×10^{12}\] electrons. The charge density on the conductor's surface equals:
Given that \[q_e=1.6×10^{-19} c\]

\[𝛿= 1.6 ×10^{-6} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[𝛿= 4.8 ×10^{-6} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[𝛿= 3.6 ×10^{-6} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[𝛿= 6 ×10^{-6} \;\;c/m^2\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution Choose the correct answer

A semi-cylinder made of insulating material with small base radius (0.1 m) and large base radius (0.2 m) was placed in a uniform electric field as shown in the figure below with intensity \[500\;\;N/C\]. The flux passing through the lateral surface of the semi-cylinder equals:

\[∅=47.1 \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ ∅=0.0 \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[∅= 25.3\;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[∅= - 35.2 \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show solution
Click here to show solution Choose the correct answer

A cube has a point charge at its center with a magnitude of
\[8 ×10^{-9}c\]. The flux through the top and bottom surfaces is equal to
\[ 𝓔_0=8.85 ×10^{-12}C.m/v\]
\[∅= 432 \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-C\] |
\[ ∅=151 \;\;N.m^2 \;\;\;\;\;\;-A\] |
\[∅= 512\;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-D\] |
\[∅= - 301 \;\;N.m^2/C\;\;\;\;\;\;-B\] |
 Click here to show the solution
Click here to show the solution
Choose the correct answer
Solve the following problems

Two point charges on a straight line each with magnitude \[q_1=8\;\;nc\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; q_2=?\]The electric field was calculated at point \[A\] and its magnitude was \[E_{net}=500 \;\;N/C\]From the figure information and previous data What is the type of \[q_2\]
 \[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
Calculate the magnitude of charge \[q_2\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
Calculate the magnitude of charge \[q_2\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
\[........................................................................................\]
 Physics
Physics